Development documentation (69-SNAPSHOT)
This is the documentation for the current development state of the BasePOM project. All information in here reflects the current state of development on the main branch and is subject to change until it has been released as a numbered version.
1. Introduction
The BasePOM project aims to make using Apache Maven as a build tool painless. It provides a set of well-known plugins for Apache Maven with an opinionated base configuration and a number of configuration options. It is aiming at Java projects but can easily be extended for other languages that are supported by Apache Maven.
It provides base configurations for unified, organization-wide build setups and supports simple project setups and complex Multi Module project use cases.
BasePOM and its private predecessors have been in use in many companies and open-source projects since 2010.
Core features of BasePOM:
-
Opinionated configuration. BasePOM Parent POMs configure Maven Plugins with reasonable defaults
-
Property-based customization. BasePOM Parent POMs expose a number of properties that can be customized in Child POMs or from the command line
-
Profile activation. BasePOM Parent POMs contain a number of profiles that activate under specific conditions and customize build steps or activate specific plugins
-
Policy modifications. Any aspect of a BasePOM Parent POM can be customized through Policy POMs
2. Features
BasePOM provides opinionated configuration for the following plugins:
-
packaging plugins: assembly, jar, javadoc, repack, source, shade, jxr
-
build quality: enforcer, dependency, dependency-management, dependency-scope, dependency-versions-check, duplicate-finder, spotbugs, pmd, checkstyle, jacoco, license
-
tools: build-helper, property-helper, git-commit-id, really-executable-jar
-
release and site: scm, release, gpg, central-publishing
-
site building: site, scm-publish, project-info-reports
Most of the plugins are configured with reasonable defaults and might not need to be changed.
BasePOM provides:
-
defaults for build lifecycle setup and phases
-
defaults for unit and integration test execution
-
defaults for code quality checks and static code analysis
-
locked versions for auxiliary tool libraries
-
locked versions for Maven plugins
|
As the BasePOMs stack on top of each other, some features are only available in |
2.1. BasePOM Maven Plugins
The BasePOM project maintains a number of Apache Maven plugins that are useful outside the BasePOM project as well:
-
dependency-versions-check — verifies that the resolved versions of project dependencies are mutually compatible to each other
-
duplicate-finder — Finds and flags duplicate and conflicting classes and resources on the java classpath
-
property-helper — generate and manipulate properties during the build process
-
inline — inlines dependencies into a main artifact by rewriting classes and resources
-
repack — repacks code and its dependencies into a single archive for applications and services
-
dependency-management — validates that the versions in dependency management and plugin management match the resolved versions
-
dependency-scope — ensures that tests scoped dependencies do not override dependencies in compile scope
3. Overview
The Apache Maven documentation is vast, very disjointed and spread across many micro-documentation sites, often outdated and generally hard to understand. As a result, Apache Maven projects often "grow" out of a home-made set of plugins which got copied from some other project and then augmented by looking at StackOverflow. Maven builds become hard to understand and often undermaintained.
Even though there have been a number of attempts to improve the documentation situation, getting a Maven build going is often dreaded by developers.
None of that is a fundamental Maven problem. Setting up Maven is much easier than setting up build tools that require programming or scripting. And POM inheritance allows centralized setup for many aspects of a build.
3.1. Requirements
-
Java 17 is the minimal version for building. It is highly recommended to use the latest Java LTS version (Java 21) to execute the build process. Each of those Java versions can build project artifacts that are compatible with JDK version 7 or later.
-
Apache Maven 3.9.0 is the minimal version for building. It is recommended to use the latest Apache Maven 3.x.x.
| Apache Maven 4 has reached the RC stage, and there might be a release soon. BasePOM will provide a separate set of POMs for Apache 4 once it has been released. The main branch will stay compatible with Apache Maven 3 until version 4 has reached sufficient adoption within the Java community. |
3.2. Releases and compatibility
BasePOM uses single-digit versioning for releases. Every release is a major version, and while there is an effort to keep releases backwards compatible, it is only an effort, not a goal. Any change in a BasePOM release is listed in the CHANGES file on GitHub.
Build systems are generally stable, and there should be no need to upgrade the BasePOM version unless there are compatibility issues with the current version, features from a newer version needed or known security problems.
3.3. License
All BasePOM code is released under the Apache Software License Version 2.0.
4. Glossary
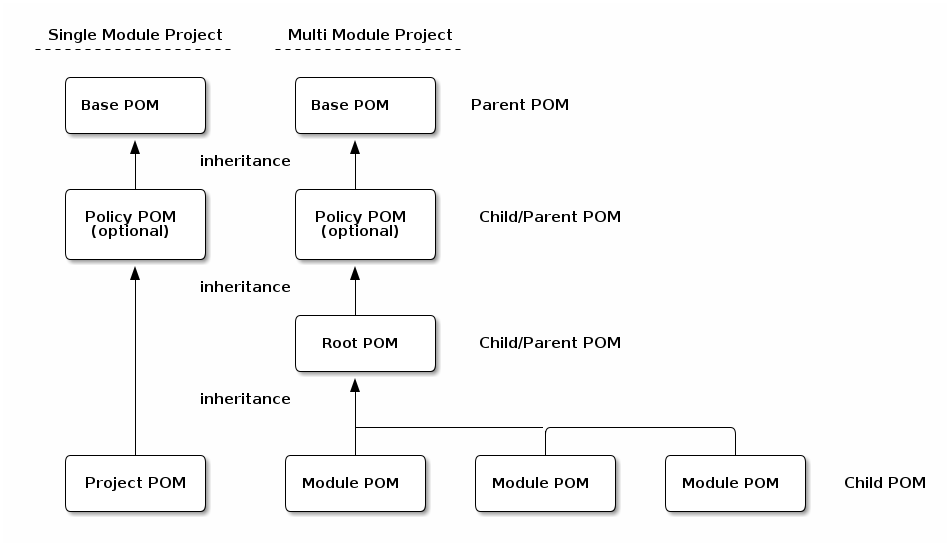
- Single Module Project
-
A Maven project that contains only a single POM file in its root directory. This POM file does not contain a
<modules>section. - Multi Module Project
-
A Maven project that is structured into multiple build units. The POM file in the root directory contains a
<modules>section and directories with additional POM files. - POM
-
Project object model. The configuration file which is read by the Apache Maven build tool to execute build steps for a project. A standard POM file is structured using XML and is named
pom.xml. - Child POM
-
A POM file that contains a
<parent>section and inherits configuration from the referenced POM file. - Parent POM
-
A POM file that is referenced by a child POM.
- Root POM
-
The POM file in the root directory of a Multi Module project.
- Base POM
-
A Parent POM file that defines configuration and policy for many projects.
- Policy POM
-
A POM file that inherits from a Base POM file and configures specific policies e.g., for an organization. A policy POM in turn serves as a Base POM for an organization.
5. BasePOM starting points
BasePOM contains the following Parent POMs:
- foundation
-
The
foundationPOM provides an opinionated base configuration but not any code-specific policies. It sets the Maven plugins up for further configuration in a specific Policy POM. It is intended as a starting point when putting together an organization-specific Policy POM. Projects will rarely use this directly.
Usage:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.basepom</groupId>
<artifactId>basepom-foundation</artifactId>
<version>69-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
...
</project>- minimal
-
This is a bare-bones Policy POM that defines a small set of policies. It can be used directly for projects that do not need a lot of scrutiny. For larger projects, a custom Policy POM should be defined which can be built on top of the
minimalBasePOM.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.basepom</groupId>
<artifactId>basepom-minimal</artifactId>
<version>69-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
...
</project>- oss
-
A Policy POM for releasing and distributing projects through the Sonatype OSS repository. It can be used as a parent POM for projects that distribute their artifacts through OSS. The plugin uses the Sonatype Nexus staging plugin by default to deploy a project to OSS.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.basepom</groupId>
<artifactId>basepom-oss</artifactId>
<version>69-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
...
</project>6. Customizations using Maven properties
BasePOM provides a set of properties that configure the various Maven plugins. The default values have been chosen so that they make sense for most projects.
Each property can be overridden from the command line, a Policy POM or a project-specific POM file.
All properties are namespaced using the . separator.
-
All BasePOM specific properties begin with
basepom. -
Properties that define the version of a library or a dependency begin with
dep.and end with.version -
Properties that define the version of a Maven plugin begin with
dep.plugin.and end with.version
Project customization overrides these properties in Policy or Project POM files. The following tables
contain a customization column that gives some guidance how common these values are modified:
- often
-
This is a default value that works for some projects. It is common for a Project or Policy POM to override it.
- sometimes
-
This is a default value that works for most projects. Project or Policy POMs can override it, but most don’t.
- rarely
-
The default value should work for almost every project. Only in very specific cases is it overridden by a Project or Policy POM.
- policy
-
This is a value often modified as part of a larger, organization-wide policy set of customizations.
- profile
-
This value is often controlled through specific profile activation.
6.1. Setting the JDK version
Basepom supports different JDK versions for running the tool chain, compiling the main and the test sources:
| project.build.systemJdk | 17 |
often | foundation | Minimal JDK version for running the Apache Maven tool chain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
project.build.targetJdk |
|
often |
foundation |
Target JDK version. Source code will be compiled to this JDK version. |
project.build.testJdk |
|
rarely |
foundation |
Test JDK version. Test source code will be compiled to this JDK version. |
By default, all three values are identical.
6.2. Standard Maven Properties
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
project.build.sourceEncoding |
|
rarely |
foundation |
Character encoding for source files. |
project.reporting.inputEncoding |
|
rarely |
foundation |
Character encoding for all files read when generating reports. |
project.reporting.outputEncoding |
|
rarely |
foundation |
Character encoding for all reporting files generated by Maven. |
maven.compiler.source |
|
rarely |
foundation |
The source code specification used in this project. |
maven.compiler.target |
|
rarely |
foundation |
The target bytecode specification used in this project. |
maven.compiler.release |
|
rarely |
foundation |
The release JDK version used in this project. |
|
The |
6.3. Global properties
These properties affect multiple plugins. POMs that add new plugins should evaluate these properties if necessary and not define plugin-specific properties.
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.build.maxheap-mb |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
Sets the maximum heap in MB for plugins. This value has no qualifier, so it can be used in plugins that do not take a unit in their configuration value. |
basepom.build.jvmsize |
|
rarely |
foundation |
Sets the maximum heap size for plugins that take a qualifier. This value is rarely modified directly, but uses the value set in |
basepom.site.skip |
|
often |
foundation |
If set to |
basepom.maven.version |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
The minimum required version for Apache Maven. |
6.4. Plugin customizations
These properties control settings for specific plugins. Most plugins have an opinionated default configuration with very little need for further customization. Where it is useful, these customizations are exposed as properties that can be changed in a Project or Policy POM.
Properties are usually grouped by prefix.
6.4.1. Compilation control
Language compilers should support all properties in this section. By default, BasePOM uses the maven-compiler-plugin for Java.
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.compiler.fail-warnings |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
Fail compilations if warnings are present. |
basepom.compiler.parameters |
|
rarely |
foundation |
Generate metadata for reflection on parameter names. By default, this is activated. |
basepom.compiler.use-incremental-compilation |
false |
sometimes |
foundation |
If a language compiler supports incremental compilation, it should use this property for control. The compiler plugin supports this flag. |
6.4.2. Artifact installation, deployment and release customization
Besides building, Apache Maven can install the resulting artifacts into the local repository or deploy them to a remote repository. Releasing an artifact is creating a stable, immutable build with a version that does not end in -SNAPSHOT. All steps of the Apache Maven lifecycle can be customized with the following properties:
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.at-end |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
Set the default value for installing and deploying artifacts in the build cycle for Multi Module projects. If |
basepom.at-end.install |
|
rarely, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.at-end.deploy |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.central-publishing.skip |
|
rarely |
oss |
If |
basepom.central-publishing.fail-build |
|
rarely |
oss |
If |
basepom.central-publishing.repo-id |
|
rarely |
oss |
The repository Id used to look up credentials in |
basepom.central-publishing.auto-publish |
|
rarely |
oss |
If |
basepom.central-publishing.wait-until |
|
rarely |
oss |
|
basepom.central-publishing.checksums |
|
rarely |
oss |
Controls the creation of checksums for the uploaded artifacts. |
basepom.central-publishing.deployment-name |
|
rarely |
oss |
Name of the deployment on the central dashboards. |
basepom.deploy.snapshot.repo-id |
|
sometimes, policy |
oss |
Defines the snapshot repository id for deployments. Defaults to |
basepom.deploy.snapshot.url |
sometimes, policy |
oss |
Defines the snapshot repository URL for deployments. |
|
basepom.deploy.skip |
|
rarely |
foundation |
If |
basepom.install.skip |
|
rarely |
foundation |
If |
basepom.release.profiles |
|
rarely |
oss |
Sets the name of one or more release profiles. Multiple release profiles must be comma-separated. By default, the |
basepom.release.push-changes |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
If |
basepom.release.tag-name-format |
|
often |
foundation |
Name tag format for the release tag. See the Maven Release Plugin Documentation for details. |
basepom.release.preparation-goals |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
Defines the goals run by maven when executing |
6.4.3. Javadoc Generation
Javadoc artifacts are created as part of the build lifecycle. While they are optional, some distribution sites (OSS, Maven Central) require the creation of a Javadoc artifact.
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.javadoc.skip |
|
often, profile |
foundation |
If |
basepom.javadoc.doclint |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
Controls the |
basepom.javadoc.exclude-package-names |
`` |
sometimes |
foundation |
Allows the exclusion of package names from Javadoc generation. See Maven Javadoc plugin documentation for the exact syntax. |
basepom.javadoc.show |
|
rarely, policy |
foundation |
Controls the access level included in the Javadocs. |
basepom.javadoc.legacy-mode |
|
often |
foundation |
Controls whether Javadoc generation uses the classpath or module path when building post-java 8 projects. Unless a project defines module descriptors, legacy mode should be used. |
basepom.javadoc.title |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
Controls the title for the Javadoc API documentation. |
6.4.4. Unit Tests
The Apache Maven surefire plugin is active by default. Any other test plugin should also use these properties.
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.test.arguments |
`` |
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
Allows additional arguments for the |
basepom.test.skip |
|
often, profile |
foundation |
If |
basepom.test.fork-count |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
Controls the number of parallel tests to run. The default is 3/4 of reported CPU cores. |
basepom.test.reuse-vm |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.test.timeout |
|
often |
foundation |
Maximum time in seconds that a unit test can run. |
basepom.test.memory |
|
often |
foundation |
Memory for each forked VM. |
basepom.test.groups |
`` |
sometimes |
foundation |
Test group selection for unit tests. |
6.4.5. Integration Tests
Apache Maven supports multiple plugins for integration tests. BasePOM supports the failsafe and the invoker plugin for integration tests.
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.it.arguments |
`` |
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
Allows additional arguments for the |
basepom.it.skip |
|
often, profile |
foundation |
If |
basepom.it.skip-install |
|
often, profile |
foundation |
If |
basepom.it.test-scope |
|
often, profile |
foundation |
Sets the maven resolution scope to decide which artifacts are installed in the integration test repository. The default is 'all artifacts' in the test scope. |
basepom.it.memory |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
Memory allocated for each integration test VM. |
basepom.it.fork-count |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
Controls the number of parallel tests to run. Default is 1/2 the number of reported CPU cores. |
basepom.it.timeout |
|
often, policy |
foundation |
Maximum time in seconds that an integration test can run. |
basepom.it.groups |
`` |
sometimes |
foundation |
Test group selection for integration tests. |
|
rarely |
foundation |
Base directory where all integration tests are located. |
|
basepom.failsafe.reuse-vm |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
If |
6.4.6. git version control support
BasePOM uses the git-commit-id-maven-plugin to provide scm information to the build. The main use case to modify its configuration is if the code base does not use git.
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.git-id.skip |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.git-id.skip-pom-projects |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
If |
basepom.git-id.fail-no-git |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.git-id.fail-no-info |
|
rarely, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.git-id.use-native |
|
rarely |
foundation |
Use the system installed |
basepom.git-id.run-only-once |
|
rarely, policy |
foundation |
Execute only once for a Multi Module project build. This is almost never the right thing: If the build uses a |
basepom.git-id.date-format |
|
rarely, policy |
foundation |
Timestamp format as defined for |
basepom.git-id.date-format-timezone |
|
rarely, policy |
foundation |
Timezone for the timestamp defined with the |
6.4.7. Executable support
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.executable.flags |
sometimes |
foundation |
command line parameters for the |
|
basepom.executable.name |
|
rarely |
foundation |
Sets the name of the executable. |
basepom.shaded.main-class |
(empty) |
deprecated |
minimal |
Defines the main class for a shaded jar (using the |
basepom.main-class |
|
often |
minimal |
Defines the main class for the executable jar when shading or repacking an artifact. |
6.5. Setting plugin and dependency versions
Each BasePOM release defines the versions for all Maven plugins and dependent libraries. The values change from release to release and are chosen based on the stability and release quality of the various tools.
These versions can be overwritten in Policy POMs, project POMs or the command line.
| Property Name | defined in | comment |
|---|---|---|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
oss |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
oss |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
oss |
|
|
oss |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
oss |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
|
|
foundation |
Checkstyle library version, used by the checkstyle plugin |
|
foundation |
Dependency Analyzer library version, used by the dependency plugin |
|
foundation |
PMD library version, used by the PMD plugin |
|
foundation |
Spotbugs library version, used by the spotbugs plugin |
|
minimal |
BasePOM policy jar version |
7. URL inheritance
The BasePOM project is designed to work with the git SCM repositories. Unlike other SCMs, git has a single URL for the SCM which is valid for all modules within a multi-module build.
BasePOM turns off the "url inheritance" scheme in the poms and the <scm> settings to match git behavior. If this is not desired, add the following attributes to a policy pom:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"
child.project.url.inherit.append.path="true">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.basepom</groupId>
<artifactId>basepom-{flavor}</artifactId>
<version>69-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<scm child.scm.connection.inherit.append.path="true"
child.scm.developerConnection.inherit.append.path="true"
child.scm.url.inherit.append.path="true"
...
</scm>
...
</project>This restores the default behavior. These attributes are documented as part of the Maven Model Builder and supported with all current versions of Maven 3.
8. Code quality and Build checkers
BasePOM brings a set of preconfigured plugins to check the quality of the code base and ensure that the resulting artifacts are valid. The following plugins are supported:
-
Maven Enforcer — Basic checks for Build JDK, Maven version etc. ("The Loving Iron Fist of Maven™")
-
Maven Dependency Plugin — Ensure declared and used dependencies.
-
Duplicate Finder Plugin — Test for duplicate classes on the class path which threaten build stability
-
Dependency Management Plugin — Ensure that plugins and dependencies are declared in
pluginManagementanddependencyManagementsections -
Dependency Scope Plugin — Ensure that transitive dependencies are not accidentally declared in
testscope. -
Dependency Versions Check Plugin — Ensure that multiple dependency references with different versions converge.
-
Spotbugs — Run the spotbugs code quality tool.
-
Coverage — Use the jacoco code coverage tool.
-
Maven PMD — Run the PMD code quality tool.
-
Maven Checkstyle — Run the checkstyle code formatting and checker tool.
-
Maven Javadoc — Lint the Javadoc included in the source code.
-
License check plugin — Ensure that source code files contain correct license headers.
All checkers are optional. Each checker can fail the build if it detects a problem.
Execution of each checker is controlled by a basepom.check.skip-<name> property. If this is set to true, the checker will not be executed.
Build failure is controlled through a basepom.check.fail-<name> property. If this is set to true, any error detected by the checker will fail the build.
| Checker | enabling/disabling property | property for enabling/disabling build failure |
|---|---|---|
Checker groups |
||
all checkers |
|
|
basic checkers |
|
|
extended checkers |
|
|
Individual checkers |
||
Maven checkstyle |
|
|
Jacoco |
|
|
Maven Enforcer |
|
|
Maven Dependency |
|
|
Dependency Management |
|
|
Dependency Scope |
|
|
Dependency Version Check |
|
|
Duplicate Finder |
|
|
License |
|
|
Maven PMD |
|
|
Spotbugs |
|
|
Javadoc |
|
|
|
Javadoc is special because it generates an artifact but also provides checking ("linting") of the Javadoc blocks in the source code. Javadoc generation is
often controlled independently of checker runs, so it is not part of the |
8.1. Checker hierarchy
The different checkers are grouped together but can also be individually controlled. By default,
the group properties basepom.check.skip|fail-basic and basepom.check.skip|fail-extended inherit the value of the basepom.check.skip|fail-all properties:
<properties>
<basepom.check.skip-all>false</basepom.check.skip-all>
<basepom.check.skip-basic>${basepom.check.skip-all}</basepom.check.skip-basic>
<basepom.check.skip-extended>${basepom.check.skip-all}</basepom.check.skip-extended>
<basepom.check.fail-all>true</basepom.check.fail-all>
<basepom.check.fail-basic>${basepom.check.fail-all}</basepom.check.fail-basic>
<basepom.check.fail-extended>${basepom.check.fail-all}</basepom.check.fail-extended>
</properties>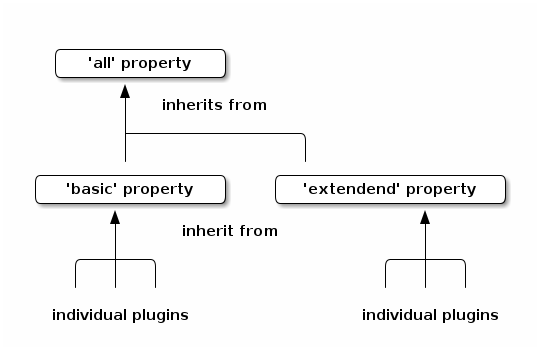
Changing the all property also affects all its children. Parent or Policy POMs can override these properties to attach or detach a checker from a group.
The foundation BasePOM defines the following groups:
-
all— contains allbasicandextendedchecks. -
basic— containsenforcer,dependency,duplicate-finder,dependency-management,dependency-scopeanddependency-versions-check -
extended— Depends on the different BasePOM types:-
spotbugsandcoveragefor thefoundationBasePOM -
spotbugs,coverage,pmd, andcheckstylefor theminimalBasePOM -
spotbugs,coverage,pmd,checkstyleandlicensefor theossBasePOM
-
For the foundation BasePOM, the pmd and checkstyle checkers are deactivated. All other checkers are active. All active checkers will fail the build if an error is detected.
8.2. Checker execution phases
While some checkers rely on class files, others only look at source code or configuration. These checkers can be executed before compilation ("early") or after compilation and test execution ("late").
There are good reasons for either:
-
early execution avoids long compile times and then checkers failing the artifact generation
-
late execution allows the execution of the compilation and test lifecycle phases without having to continuously fix unrelated problems (e.g., dependencies or code style issues).
The following plugins can be configured for early (use validate) or late (use verify) execution. By default, all checkers are run late (in the verify phase).
| Checker | Property Name |
|---|---|
Dependency Version Check |
|
Dependency Management |
|
Dependency Scope |
|
Maven Dependency |
|
Maven checkstyle |
|
License |
|
8.3. Checker customization
Most checkers are self-contained and need no additional configuration. Others (especially PMD and checkstyle) require extensive policy configuration (see the Creating a PolicyPOM to apply a build policy section).
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.check.checkstyle-severity |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
Controls which severity levels are considered a violation. Only violations fail the build. Valid values are |
basepom.dependency-management.allow-versions |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.dependency-management.allow-exclusions |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.dependency-management.dependencies |
|
often, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.dependency-management.plugins |
|
often, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.dvc.direct-only |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
Only report direct dependencies of a project, not all dependencies |
basepom.pmd.fail-level |
|
sometimes, policy |
foundation |
Minimum PMD violation level that will fail the build |
basepom.license.header |
|
often, policy |
oss |
The license header to use. This is a reference to a file or a resource on the plugin classpath |
basepom.license.skip-existing |
|
sometimes, policy |
oss |
Keep existing license headers, do not replace them |
basepom.gpg.use-agent |
|
rarely |
oss |
Use the GnuPG agent to manage private signing keys |
9. Build cycle
BasePOM configures all the Maven plugins as part of the Maven build lifecycle. Being configured is different from execution, though. Plugin execution can be skipped for many reasons; most common is that the plugin configuration has a skip property set.
| Plugin | Phase | execution id | goal(s) | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
validate |
basepom.default |
revision |
fetch SCM revision information |
|
validate |
basepom.default |
get |
create build-specific ids |
|
validate |
basepom.default |
enforce |
enforce maven and jdk version |
|
process-resources |
default-resources |
resources |
prepare main resources |
|
compile |
default-compile |
compile |
compile main sources |
|
process-test-resources |
default-testResources |
testResources |
prepare test resources |
|
test-compile |
default-testCompile |
testCompile |
compile test sources |
|
process-test-classes |
basepom.default |
prepare-agent |
prepare test coverage agent |
|
test |
default-test |
test |
run unit tests |
|
package |
default-jar |
jar |
package main artifact |
|
package |
basepom.default |
test-jar |
package test artifact |
|
package |
basepom.default |
jar |
package javadocs / run javadoc linter |
|
package |
basepom.default |
jar-no-fork |
package main sources |
|
package |
basepom.default |
test-jar-no-fork |
package test sources |
|
validate/verify |
basepom.default |
analyze-only |
build checker |
|
validate/verify |
basepom.default |
analyze-duplicate |
build checker |
|
validate/verify |
basepom.default |
analyze-dep-mgt |
build checker |
|
validate/verify |
basepom.default |
check |
build checker |
|
validate/verify |
basepom.default |
analyze |
build checker |
|
validate/verify |
basepom.default |
check |
build checker |
|
verify |
basepom.default |
check |
build checker |
|
verify |
basepom.default |
check |
build checker |
|
verify |
basepom.default |
check |
build checker |
|
validate/verify |
basepom.default |
check |
build checker |
|
install |
default-install |
install |
install artifacts in the local repository |
|
deploy |
default-deploy |
deploy |
deploy artifacts to remote repository |
9.1. Build profiles
A BasePOM may contain additional profiles that configure plugins or add goals to the lifecycle.
9.1.1. basepom.invoker-integration-testing (foundation)
This profile activates if the build module contains a src/it directory.
|
Due to a limitation in Apache Maven is the |
This profile adds the following goals to the lifecycle:
| Plugin | Phase | execution id | goal(s) | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
pre-integration-test |
basepom.default-it |
prepare-agent-integration |
prepare integration test coverage agent |
|
integration-test |
basepom.invoker-integration-testing.default |
install |
install integration test prerequisites |
|
integration-test |
basepom.invoker-integration-testing.default |
integration-test |
run integration tests |
|
integration-test |
basepom.invoker-integration-testing.default |
verify |
verify integration test results |
9.1.2. basepom.executable (foundation)
This profile activates if a .build-executable file exists in the current build module. This file only needs to exist, it can be empty.
|
This profile is experimental. While it is possible to build executables, there are some shortcomings that will be addressed in the future. The plugins in this profile may be replaced with other plugins. |
This profile adds the following goals to the lifecycle:
| Plugin | Phase | execution id | goal(s) | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
package |
basepom.executable.default |
shade |
create a jar with all dependencies included |
|
package |
basepom.executable.default |
really-executable-jar |
create an executable from the shaded jar |
9.1.3. basepom.repack (foundation)
This profile activates if a .repack-executable file exists in the current build module. This file only needs to exist, it can be empty.
|
This profile is experimental. While it is possible to build executables, there are a number of configuration options of the |
This profile adds the following goals to the lifecycle:
| Plugin | Phase | execution id | goal(s) | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
package |
basepom.repack.default |
repack |
repacks the main artifact with all dependencies |
|
package |
basepom.repack.default |
really-executable-jar |
create an executable from the repacked jar |
9.1.4. basepom.central-release (oss)
This is the release profile for releasing an artifact to the Maven central repository. As the old OSS service is sunset and will be turned off, this is now the default release profile. It is configured as release profile for the release plugin if the oss BasePOM is used. It gets activated when executing the release:perform goal of the release plugin.
This profile uses the Central Publishing Plugin, which is now the recommended way of publishing software to the Central repository.
-
disables the regular
maven-deploy-plugin -
skip unit tests (all tests have already passed as part of the release process)
-
skip all checkers that are following the
basepom.check.skip-allsetting (they have already been executed as part of the release process) -
always create a
javadocartifact
This profile does not use the <distributionManagement> section of a project pom. The deployment repositories are configured using the basepom.deploy.snapshot.repo-id property for snapshots and basepom.central-publishing.repo-id for release artifacts. It uses central as the repository id for both snapshots and releases. The local settings.xml file must contain credentials for it to authenticate for artifact upload.
This profile adds the following goals to the lifecycle:
| Plugin | Phase | execution id | goal(s) | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
verify |
basepom.release.default |
sign |
creates the GPG signature for releasing to OSS |
|
deploy |
basepom.release.default |
publish |
publish the artifact to the central repository staging area. |
9.1.5. basepom.invoker-reporting (oss)
This profile activates if the build module contains a src/it directory.
|
Due to a limitation in Apache Maven is the |
This profile adds the following reports to the site build:
| Plugin | Report |
|---|---|
|
report |
|
report-integration |
10. Creating a PolicyPOM to apply a build policy
Most organizations create internal policies on how builds should be organized, what rules should be enforced etc. Having such policies codified and enforced by the build system is a massive boost for code quality and reuse.
An organization that plans to use BasePOM should also create an organization-specific Policy POM.
BasePOMs were designed specifically to allow policy enforcement across many projects. The minimal and oss BasePOMs are examples on how to create Policy POMs for projects to use.
A PolicyPOM should define or apply specific rules for
-
property settings (e.g., required JDK level, checker settings, etc.)
-
remote repositories for artifacts and artifact deployment
-
specific checker configuration
-
code packaging
-
Unit and integration test configuration
-
Policy profiles
10.1. The minimal Policy POM
When using the minimal BasePOM for a project, some policies are applied:
-
The
pmdandcheckstylecheckers are added to theextendedset of Build checkers. -
Rule configuration for
pmd,checkstyleandspotbugs -
a repository reference is added that fixes a problem with the popular Spring framework
-
rules for the
duplicate-finderbuild checker -
rules for the
dependency-checkersbuild checker -
configuration for the
shadeplugin -
environment variables for unit and integration tests
The minimal BasePOM uses a policy jar to store the configuration for spotbugs and checkstyle.
10.1.1. duplicate-finder plugin configuration
The duplicate-finder plugin will flag any class that appears multiple times on the class path (in multiple jars). While this is generally desirable, there are some common jars that contain the same classes. Almost all of these overlaps are specific to annotation classes.
| package | related dependencies (jars that may contain these classes) |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Similar to classes, there are other resources on the class path as well. Most of these resources should be unique. However, there are a few resources that are often packaged into jars where duplicates can be tolerated.
The following resource patterns are ignored:
-
any resource ending with
.afm,.dtd,.gif,.html,.java,.png,.properties,.txt -
any resource starting with
.about. -
any resource in a directory named
about_filesorlicense -
resources called
schemain any directory -
resource named
mime.types,plugin.properties,plugin.xml,reference.conf,log4j.xml,log4j.properties,logback.xml,logback.properties
10.1.2. pmd plugin configuration
PMD does code analysis and flags common programming errors and antipatterns. This is useful for code that is actually written but less so for code that is auto-generated where the constructs in auto-generated classes cannot be modified unless the code generator itself is changed.
Auto-generated code is usually located in target/generated-sources/stubs and target/generated-sources/annotations. These folders are excluded from being scanned by PMD.
10.1.3. dependency plugin configuration
Similar to the duplicate-checker, the dependency plugin checks what elements are on the class path and whether these are used. This process is more difficult for elements that need to be present at compile time but not at runtime and that are not referenced from the build artifacts.
For the minimal BasePOM, the dependency plugin is configured to:
-
ignore all non-test scoped dependencies in "test" scope
-
allow the following dependencies on the classpath even if there are no direct references in the resulting artifacts (all of these jars are "annotation-only" jars)
| dependency |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.1.4. shade plugin configuration
The shade plugin is used to "shade" a build artifact and all its dependencies into a single "fat jar" by rewriting packages and classes.
In the minimal Policy POM, the shade plugin is configured to
-
support
basepom.main-classto configure main class for a shaded jar -
collect all additional, named sections from dependencies into the shaded jar
-
create the
X-BasePOM-Build-Idmain manifest entry from the${basepom.shaded.id}to differentiate a shaded jar from the original, non-shaded jar
10.1.5. repack plugin configuration
The repack plugin can create a "fat jar" artifact from a build artifact by including all its dependencies in a single jar. It does not rewrite any classes or unpack dependencies.
In the minimal Policy POM, the repack plugin is configured to
-
support
basepom.main-classto configure main class for a repacked jar
10.1.6. surefire and failsafe plugins
The minimal BasePOM adds a few system properties for testing.
| property | value | function |
|---|---|---|
|
|
This setting is used by the JVM to encode/decode file paths |
|
|
user timezone for tests |
|
|
tests run without a graphical UI |
|
|
formatter for java.util.logging messages |
10.2. The oss Policy POM
The oss BasePOM is intended for projects that distribute their artifacts through the Sonatype OSS ecosystem to Maven Central. In addition to the minimal policy, it applies the following configuration:
-
The
licensechecker is added to theextendedset of Build checkers. -
Configures the OSS repositories for snapshot and release distribution. This differs based on the release profile. See below for a description of the available repositories. The
ossBasePOM also adds the following goals to the lifecycle:
| Plugin | Phase | execution id | goal(s) | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
validate / verify |
basepom.default |
check |
check license headers |
11. Reproducible Builds with BasePOM
Apache Maven supports reproducible builds (where it is possible to create bit-identical artifacts from a given SCM revision) as described in the reproducible build mini-guide. Apache Maven writes a timestamp into a build property (project.build.outputTimestamp) and any plugin is expected to create reproducible output when this property is present.
BasePOM supports reproducible builds in version 59 or higher.
11.1. Using the git SCM information for reproducible builds
It is possible to create reproducible builds for any git commit using BasePOM. In every POM in a project, add
<properties>
<project.build.outputTimestamp>${git.commit.time}</project.build.outputTimestamp>
</properties>This uses the commit timestamp of the current commit as the timestamp for the reproducible build. BasePOM configures the format of the timestamp to be compatible to the project.build.outputTimestamp property and executes the git-commit-id plugin as the first plugin in the build cycle, therefore ensuring that all other plugins will pick up the setting correctly.
11.2. Using POM inheritance with the git SCM information
While the artifact:check-buildplan goal recommends not using POM inheritance for the project.build.outputTimestamp property, it can be used in combination with the git.commit.time value. By default, the
git-commit-id plugin will skip execution for a POM project, so the value may not be set correctly. To avoid this, activate the plugin for POM projects as well by adding the following properties to the top-most POM:
<properties>
<project.build.outputTimestamp>${git.commit.time}</project.build.outputTimestamp>
<basepom.git-id.skip-pom-projects>false</basepom.git-id.skip-pom-projects>
</properties>This makes a multi-module build reproducible (no additional properties in the child POMs are required).
12. Plugin configuration notes
12.1. Unit and integration tests and code coverage
The interaction between the surefire, failsafe and invoker plugin and the respective code coverage plugin (jacoco) is through an agent specification that modifies the command line for test invocation.
To hide this implementation detail, two properties exist for internal BasePOM use that should not be modified: basepom.coverage.test-args for unit tests and basepom.coverage.it-args for integration tests.
If the coverage agent is not active (by setting basepom.check.skip-coverage to true), these properties are empty. If the agent is active, it will write the necessary parameters for adding the coverage agent to these properties.
When the respective test plugin executes, they pick up the content of these properties (through the argLine configuration setting). Using a secondary property (and not the argLine property directly as most stack overflow posts would suggest) allows manual configuration on the command line while still preserving the ability to add the coverage agent through the build lifecycle.
If the argLine configuration needs to be modified (e.g., in a Policy POM), the @{basepom.coverage.test-args} (for surefire) and @{basepom.coverage.it-args} (for failsafe) must be present, otherwise this integration no longer works. Using a @ is not a typo but necessary for late evaluation of these properties.
Unfortunately, for the invoker plugin, this is not possible. For invoker, a invoker.properties file must be used which should contain the line
invoker.mavenOpts = ${basepom.coverage.it-args} -Xmx${basepom.it.memory} -Dfile.encoding=${project.build.sourceEncoding}This line emulates the argLine setting for surefire and failsafe. This property file is also late (at runtime) evaluated.
12.2. Jar properties
The maven-jar-plugin is used to create the main and test artifacts.
It is configured to create the standard implementation and specification entries as described in the Maven Jar documentation.
It also adds a number of custom entries in the jar manifest that allow inspection of build artifacts:
| Manifest entry | value | section | function |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
main |
unique build id for each artifact |
|
|
main |
project name of the build |
|
|
main |
see |
|
|
|
see |
|
|
|
see |
|
|
|
see |
|
|
|
see |
|
|
|
The artifact id of the build |
|
|
|
The group id of the build |
|
|
|
The project name of the build |
|
|
|
The version of the build |
The ${project.groupId}:${project.artifactId} section is specific for each project. This allows the maven-shade-plugin to coalesce all these sections without overwriting any of the parameters.
12.3. Shading a jar artifact
The maven-shade-plugin is used to create single artifacts with all dependencies ("fat jars") for a project.
BasePOM does not create a dependency-reduced POM. All shaded artifacts are attached. Shaded artifacts should never be used as dependencies but should be terminal (e.g., an application jar).
12.4. Repacking a jar artifact
The repack-maven-plugin is used to create single artifacts with all dependencies ("fat jars") for a project. Repacking adds all dependencies "as is" and does not change the contents of the main jar or unpacks dependencies. This produces better outcomes than shading jars.
Repacked artifacts cannot be used as dependencies as their contents are packaged into different directories.
12.5. Using the license plugin
The oss BasePOM configures the license-maven-plugin for releasing artifacts to Maven Central:
-
use the Apache Software License without the copyright line
-
map
g4,groovyandjavafiles toSLASHSTAR_STYLE -
map
stgfiles toDOUBLESLASH_STYLE -
map
xmlfiles toXML_PREFIX -
map
yamlfiles toSCRIPT_STYLE -
exclude all files in directories starting with
. -
exclude all files ending with
.md,.rst,.adoc,.sh,.txt,.thrift,.proto,.g,.releaseBackup,.vm,.st,.raw,.ser -
exclude all files in the
src/licensetree -
exclude all
CNAMEand.keepmefiles
13. Maven Site generation
The foundation BasePOM provides basic configuration for the Maven autogenerated site which summarizes information about the build lifecycle. The oss BasePOM contains the necessary reporting setup to generate a base site for a project.
| Property Name | Default Value | customization | defined in | function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
basepom.site.skip |
|
often |
foundation |
If |
basepom.site.skip-deploy |
|
often, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.site.scm.skip-deploy |
|
often, policy |
foundation |
If |
basepom.site.scm.site-path |
|
often |
foundation |
The remote repository path where the site is deployed |
basepom.site.scm.branch |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
The branch on the remote repository where the site is deployed |
basepom.site.scm.url |
<unset> |
always |
foundation |
The remote URL of the site repository |
basepom.site.scm.id |
<unset> |
always |
foundation |
The settings id used for authenticating the site repository |
basepom.site.scm.try-update |
false |
sometimes |
foundation |
If true, try a local scm update first before doing a full checkout. |
basepom.site.scm.checkout-directory |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
the local checkout directory for the site. |
basepom.site.scm.comment |
|
sometimes |
foundation |
The commit message for a site checkin. |
basepom.site.test.skip |
|
rarely |
oss |
Skip test report generation. |
basepom.site.it.skip |
|
rarely |
oss |
Skip integration test report generation. |
basepom.site.skip-checkstyle |
|
rarely |
oss |
Skip checkstyle report generation. |
basepom.site.skip-coverage |
|
rarely |
oss |
Skip coverage (jacoco) report generation. |
basepom.site.skip-pmd |
|
rarely |
oss |
Skip PMD report generation. |
basepom.site.skip-spotbugs |
|
rarely |
oss |
Skip spotbugs report generation. |
basepom.site.skip-javadoc |
|
rarely |
oss |
Skip javadoc for site generation. |
basepom.site.fail-javadoc |
|
rarely |
oss |
If |
The following reports are generated (oss BasePOM):
| Plugin | Report |
|---|---|
|
index |
|
summary |
|
dependency-info |
|
scm |
|
issue-management |
|
team |
|
modules |
|
licenses |
|
ci-management |
|
dependency-convergence |
|
dependencies |
|
dependency-management |
|
plugins |
|
plugin-management |
|
report-only |
|
checkstyle |
|
jxr-no-fork |
|
test-jxr-no-fork |
|
pmd |
|
spotbugs |
|
report |
|
javadoc-no-fork |
|
test-javadoc-no-fork |